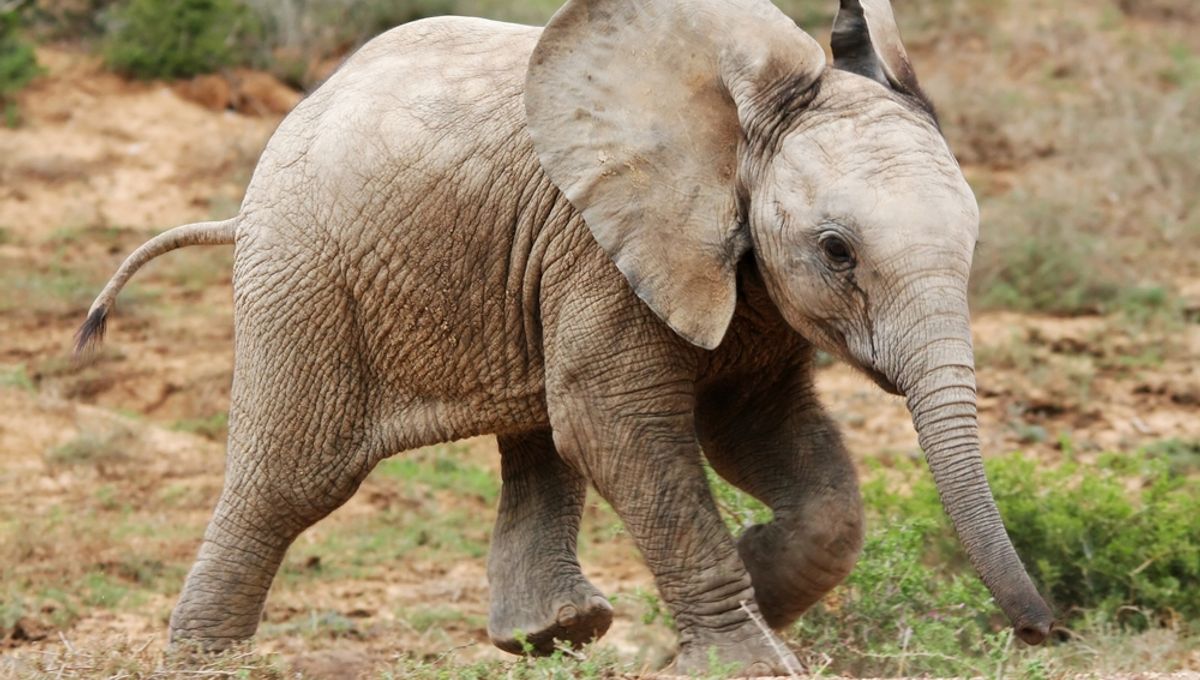
In the vast and diverse world of wildlife, certain creatures captivate our curiosity not only because of their appearance but also due to their rarity and unique origins. One such extraordinary example is Motty, the world’s *rarest elephant*. Born as a hybrid, Motty has become a symbol of genetic rarity, conservation challenges, and the marvels of biological diversity. This article delves into the fascinating story of Motty, exploring what makes this hybrid elephant so unique, the science behind his existence, and the broader implications for conservation efforts.
The Incredible Story of Motty: An Unprecedented Hybrid
Motty is recognized as the *only known elephant hybrid* of its kind. According to recent reports by , Motty’s rarity is a direct result of an extraordinary cross-breeding event that defies typical limits of elephant genetics. His origins are rooted in an unprecedented intersection of species, which has caught attention worldwide.
What Makes Motty So Special?
- Unique Hybrid Genetics: Motty’s genome contains a mix of genetic material from different subspecies or potentially even different species of elephants, making him a biological anomaly.
- Biological Rarity: As the only individual of his kind, Motty stands alone in the entire wildlife record books, highlighting the extremely rare nature of hybridization events in wild populations.
- Appearance & Characteristics: While still bearing the characteristic features of elephants, Motty exhibits some distinct physical traits that hint at his hybrid heritage, including subtle differences in ear shapes, skin texture, and size.
- Conservation Significance: His existence raises important questions about genetic diversity and the impact of habitat fragmentation on species boundaries and hybridization potential.
Understanding Elephant Hybridization
The Science Behind Hybrid Elephants
Hybridization in animals—especially among large mammals like elephants—is a rare phenomenon. Typically, elephants belong to two primary species: the African elephant (Loxodonta africana) and the Asian elephant (Elephas maximus). While hybrids between these species are infrequent, they have been documented in captivity and sometimes in the wild, particularly in regions where habitats overlap or where habitat fragmentation forces different populations into proximity.
In Motty’s case, researchers speculate that his hybrid status may involve a cross between subspecies or breeds, possibly even between geographically isolated populations. The precise genetic makeup remains a subject of ongoing research, but what’s clear is that his creation was an anomaly, unlikely to have occurred naturally in the wild on a broad scale.
Implications for Conservation
Hybrid elephants like Motty present both challenges and opportunities for conservationists. On one hand, hybridization may indicate environmental pressures, such as habitat loss or climate change, which force different populations into contact. On the other hand, hybrids can possess unique genetic traits that might be crucial for the adaptive flexibility of the species in changing environments.
However, there are ethical and ecological concerns about encouraging or allowing hybridization, as it could potentially threaten the genetic purity of distinct species. Motty’s existence emphasizes the need for careful genetic management and detailed study to understand how hybrid elephants fit into broader conservation strategies.
Motty’s Impact on Scientific Research and Public Awareness
Driving Scientific Inquiry
Motty’s rarity has catalyzed scientific interest in understanding elephant genetics, hybrid vigor, and the long-term implications of interbreeding. Conservation scientists and geneticists are particularly captivated by the prospect of learning how hybridization influences traits such as resilience, adaptability, and reproduction.
Research into individuals like Motty could shed light on the potential benefits and drawbacks of hybrid elephants, influencing future policies and management practices in zoos, sanctuaries, and wild populations.
Raising Public Awareness
Beyond the scientific community, Motty’s story captivates the imagination of the public and media worldwide. His story serves as a compelling reminder of nature’s complexity and the urgent need to protect habitats and genetic diversity. By publicizing his existence, conservation groups hope to inspire greater awareness and support for elephant conservation efforts globally.
Challenges Faced by Motty and Conservationists
While Motty’s uniqueness makes him a star in the world of wildlife, it also brings with it several challenges:
- Health and Reproduction: The long-term health and reproductive viability of hybrid elephants like Motty are still uncertain, raising concerns about their future generations.
- Habitat Preservation: Protecting the natural environments where hybrids might arise is crucial to prevent unintended genetic consequences.
- Genetic Diversity: The broader goal remains to preserve the genetic integrity of both African and Asian elephants, many of which face threats from poaching, habitat loss, and human-wildlife conflict.
Looking Toward the Future
Motty’s story is a powerful testament to nature’s unpredictable beauty and complexity. His existence challenges us to rethink conventional conservation paradigms, considering not only the preservation of species but also their genetic plasticity and adaptability. Researchers and conservationists worldwide continue to monitor Motty, hoping to unlock lessons that could benefit elephant populations globally.
As we celebrate Motty, the world’s rarest elephant hybrid, we are reminded of the importance of safeguarding our planet’s incredible biodiversity. Every creature, no matter how rare or unusual, plays a vital role in the intricate web of life.
In Conclusion
Motty stands as a unique ambassador for biodiversity, conservation, and scientific discovery. His rare hybrid status underscores the importance of habitat preservation, genetic diversity, and the need for innovative approaches to wildlife management. By learning from extraordinary cases like Motty, humanity can foster a deeper respect and responsibility toward the natural world.
For more updated news please keep visiting Prime News World.