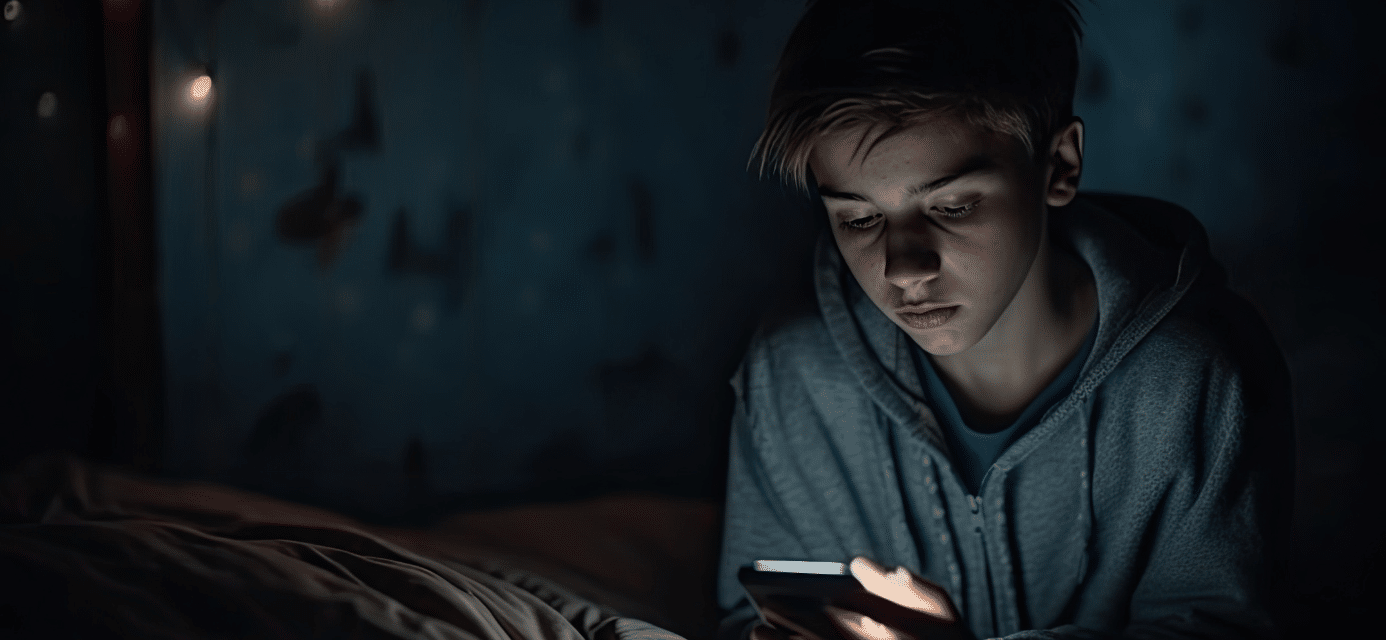
In today’s digital age, screens—smartphones, tablets, computers, and gaming devices—have become an integral part of teenagers’ daily lives. While technology offers numerous benefits, an increasing number of teens are becoming addicted to screen time, leading to significant mental health challenges. Understanding the impact of screen addiction, recognizing its signs, and exploring effective ways to help affected teens are crucial steps in safeguarding their well-being.
The Growing Concern of Screen Addiction Among Teens
Screen addiction, also known as problematic screen use, refers to a compulsive need to spend excessive hours on digital devices, often at the expense of other vital activities like social interaction, physical activity, and academic responsibilities. Recent studies and reports from Science News highlight a concerning rise in this behavior among adolescents.
Teens who are excessively engaged with screens often display signs of mental health issues, including increased anxiety, depression, and social withdrawal. The constant exposure to digital stimuli can also impair attention spans and disrupt sleep patterns, further exacerbating mental health problems.
How Screen Addiction Affects Teen Mental Health
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Overuse of screens can lead to a variety of emotional challenges, such as:
- Increased Anxiety and Depression: Prolonged screen time, especially on social media platforms, can foster feelings of inadequacy, loneliness, and low self-esteem.
- Social Isolation: While digital platforms are designed to connect, excessive use often replaces face-to-face interactions, resulting in feelings of loneliness and social disconnection.
- Impaired Emotional Regulation: Teens become less adept at managing their emotions because their interactions are mediated through screens rather than real-life experiences.
Physical and Cognitive Effects
Beyond emotional concerns, screen addiction impacts physical health and cognitive development:
- Disrupted Sleep Patterns: The blue light emitted by screens interferes with melatonin production, leading to poor sleep quality and fatigue.
- Reduced Physical Activity: Extended screen use often correlates with sedentary lifestyles, increasing risks of obesity and related health issues.
- Decline in Academic Performance: Excessive screen time can distract from studies, impair concentration, and reduce academic achievement.
Recognizing the Signs of Screen Addiction
Early detection is vital in addressing screen addiction. Parents, teachers, and caregivers should be vigilant for the following signs:
- Preoccupation with Screen Time: Constantly thinking about or planning for the next digital engagement.
- Loss of Interest in Other Activities: Neglecting hobbies, sports, or social interactions in favor of screens.
- Isolation and Withdrawal: Excessive time alone, avoiding family or friends in favor of digital devices.
- Changes in Mood and Behavior: Increased irritability, anxiety, or depression correlated with reduced screen access.
- Neglect of Responsibilities: Falling behind in schoolwork or neglecting chores because of screen use.
Strategies to Help Teens Overcome Screen Addiction
Promoting Healthy Screen Habits
Establishing balanced screen use is key. Here are practical strategies:
- Set Limits on Screen Time: Use apps or device settings to enforce daily or weekly usage caps.
- Designate Screen-Free Zones and Times: Create areas like bedrooms and dining areas where screens are off-limits, especially before bedtime.
- Encourage Alternative Activities: Promote outdoor play, sports, arts, and face-to-face social interactions.
- Model Healthy Behavior: Parents and caregivers should exemplify balanced screen use to reinforce good habits.
Fostering Emotional and Social Skills
Helping teens develop resilience and social competence can reduce dependence on digital devices:
- Open Communication: Create a safe space for teens to share feelings and discuss their digital habits.
- Encourage Real-Life Connections: Facilitate family outings, friendship-building activities, and community involvement.
- Teach Mindfulness: Introduce mindfulness exercises to help teens manage stress and emotional triggers.
Seeking Professional Support
If screen addiction persists and severely impacts mental health, consult mental health professionals. Therapy approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can be effective in addressing underlying issues and establishing healthier habits.
Conclusion
Screen addiction among teens presents complex challenges that intertwine emotional, physical, and social health. Recognizing the signs early and implementing proactive strategies can make a significant difference in a teen’s life. While technology remains an essential part of modern education and communication, moderation and mindfulness are paramount to ensuring that digital engagement supports, rather than harms, mental health.
By fostering awareness and encouraging balanced use, parents, educators, and caregivers can help teens develop healthier relationships with screens, paving the way for a more resilient and emotionally healthy generation.
For more updated news please keep visiting Prime News World.