Science continually unveils fascinating mysteries that challenge our understanding of the natural world. Recent research and discoveries have brought to light intriguing questions surrounding quantum biology, the remarkable **memories of infants**, and the extraordinary **speech abilities of parrots**. These topics, seemingly unrelated at first glance, share a common thread: they push the boundaries of our knowledge about consciousness, communication, and the fundamental processes governing life. In this blog, we will delve deep into these captivating areas, exploring current scientific insights, theories, and the ongoing debates that continue to inspire curiosity worldwide.
Quantum Biology: The Quantum Frontier in Living Organisms
Understanding Quantum Mechanics in Biological Systems
At the heart of physics lies quantum mechanics, a domain traditionally reserved for the subatomic world. Interestingly, recent studies suggest that quantum phenomena might also play crucial roles within living organisms, a field now known as quantum biology. This intriguing discipline questions whether the strange behaviors of particles—like superposition, entanglement, and tunneling—have tangible impacts on biological processes.
- Photosynthesis and Energy Transfer: One of the earliest clues pointing towards quantum effects in biology pertains to photosynthesis. Researchers have observed that plants utilize quantum coherence—an unusual state where particles are interconnected across distances—to optimize energy transfer during photosynthesis. This quantum coherence allows for the efficient harvesting of sunlight, surpassing what classical physics would predict.
- Magnetoreception in Birds: Many migratory birds possess an innate ability to navigate using Earth’s magnetic field. Scientists hypothesize that a quantum-based mechanism involving entangled electrons in proteins called cryptochromes could explain this remarkable sense, where quantum states provide directional information.
- Enzymatic Reactions and Tunneling: Quantum tunneling, where particles pass through barriers they seemingly shouldn’t, appears to facilitate certain enzymatic reactions in cells, thus speeding up biochemical processes essential for life.
While the field is still emerging, these findings hint at a profound link between quantum physics and life’s complexities. The intersection of these sciences might unlock revolutionary insights into how living systems function and evolve.
Baby Memories: The Enigma of Infant Cognition
What Do Babies Remember?
The question of whether babies can truly remember and for how long remains a topic of lively debate and research. Traditionally, it was believed that infants primarily relied on fleeting sensory impressions, with memories only developing as they grow older. However, contemporary studies challenge this notion, revealing that even newborns might possess more sophisticated memory capabilities than previously thought.
- Early Evidence of Memory: Experiments involving habituation—where infants are repeatedly exposed to stimuli—demonstrate that babies recognize and respond differently to familiar objects or sounds. For example, infants tend to show increased attention or novelty preferences when exposed to new stimuli versus familiar ones, indicating memory retention.
- Remembrance of Touch and Voice: Studies also suggest that babies can remember specific tactile experiences and voices for days or even weeks after initial exposure. This ability to retain sensory information forms the foundation of early social bonding and emotional development.
- Implicit Versus Explicit Memory: While babies may not form explicit, conscious memories like adults do, their brains are capable of implicit memory formation. This means that they can unconsciously learn patterns, preferences, and routines that influence their future behavior.
The Role of Memory in Developmental Milestones
Understanding infant memory is not just an academic pursuit; it holds vital implications for child development. Recognizing how and when babies form memories can influence parenting strategies, early education, and even interventions for developmental disorders.
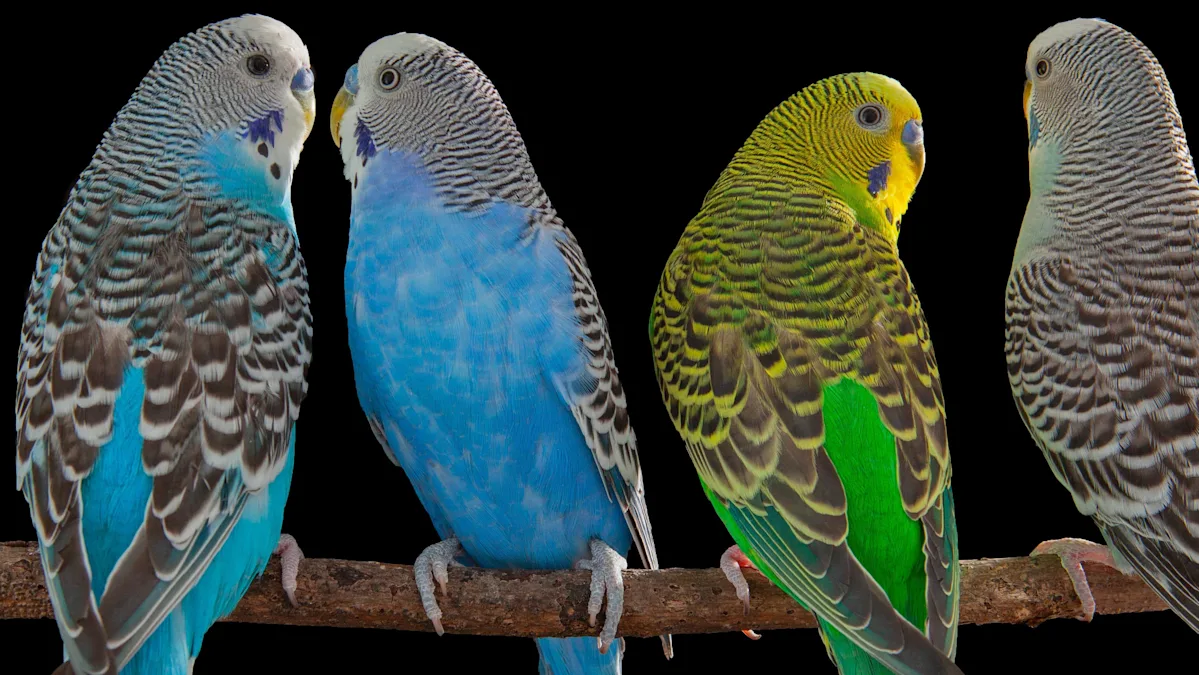
The Mysteries of Parrot Speech: Communicating with Feathers
How Do Parrots Learn to Talk?
One of the most astonishing aspects of parrots is their ability to mimic human speech. Unlike many animals that communicate through sounds or gestures, parrots demonstrate a remarkable capacity to reproduce complex sequences of words and phrases, raising questions about cognitive abilities and communication.
- Vocal Mimicry and Learning: Parrots learn through imitation, much like humans. They listen, analyze, and reproduce sounds, often mimicking words they frequently hear in their environment. This vocal plasticity is facilitated by a specialized brain region known as the “voice box,” along with a high degree of neural plasticity.
- Understanding versus Mimicry: A key debate revolves around whether parrots *understand* the meaning of the words they repeat or merely imitate sounds as a form of social interaction. Recent studies provide evidence that some parrots attach meaning to certain words, especially when linked to specific objects or requests, indicating a level of comprehension.
- The Cognitive Complexity of Parrots: Beyond speech, parrots display problem-solving skills, tool use, and social behaviors that suggest their intelligence surpasses simple mimicry. This raises profound questions about animal cognition and the extent of communication abilities in the animal kingdom.
Implications for Animal Communication
Unraveling how parrots learn and use speech sheds light on the evolution of communication and intelligence in animals. It also opens avenues for enhanced human-animal interactions, conservation efforts, and even the development of bio-inspired communication technologies.
Conclusion
From quantum effects influencing life at microscopic levels to the profound mysteries of memory in infants and the complex speech capabilities of parrots, these topics exemplify the endless curiosity that drives scientific discovery. As research progresses, we might someday fully understand how these phenomena operate, potentially revolutionizing fields like biology, neuroscience, and animal behavior.
In summary:
- Quantum biology challenges our classical view of life, revealing quantum phenomena as integral to biological functions.
- Infants might possess more advanced memory capabilities than traditionally believed, influencing early development.
- Parrots demonstrate extraordinary vocal learning and possible comprehension, offering insights into animal cognition and communication.
Continued exploration in these areas promises to deepen our understanding of the natural world and our place within it. Science not only answers questions but also sparks new inquiries, fueling our collective curiosity and quest for knowledge.
For more updated news please keep visiting Prime News World.