In a groundbreaking revelation that could potentially reshape our understanding of planetary history and the possibility of extraterrestrial life, NASA researchers have identified what appears to be multi-billion-year-old coral-like structures on the Red Planet. This discovery, documented by sources such as Live Science and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, suggests that Mars once harbored conditions suitable for complex life forms—an astonishing parallel to Earth’s own ancient marine ecosystems.
The Discovery: What Was Found on Mars?
Coral-Like Structures and Signatures of Water
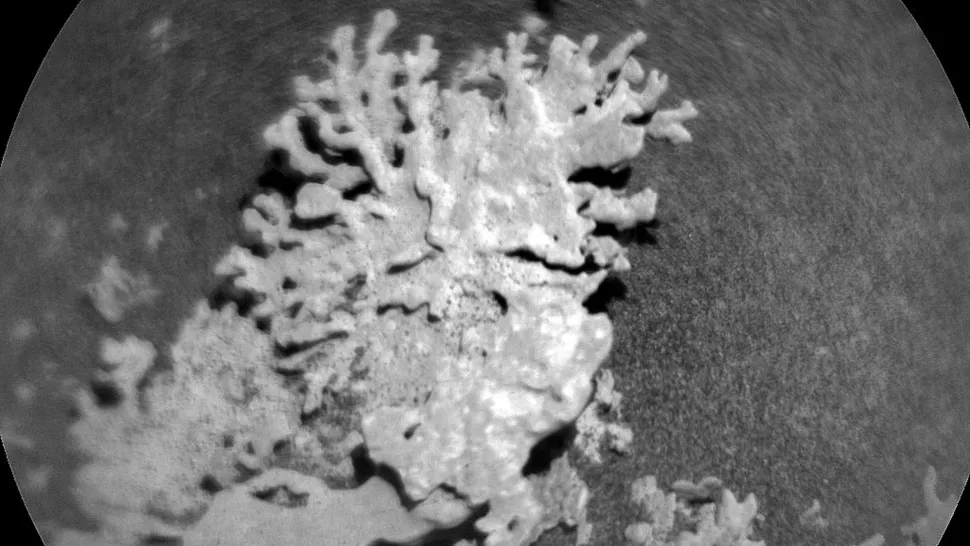
Scientists analyzing data from remote sensing instruments and rover imagery have pinpointed formations that resemble coral reefs and reef-like rocks. According to NASA reports, these formations are not random mineral deposits but exhibit structural characteristics similar to biological reef systems. The crucial evidence comes from various observations, including images captured by NASA’s Curiosity Rover, which has been exploring Gale Crater for years.
One notable example is a discovery reported by NASA’s Curiosity Rover, where researchers spotted a rock that strikingly resembles coral, dubbed a “coral reef” rock. This finding hints at the possibility that Mars once had extensive bodies of water capable of supporting such structures. The presence of these formations strongly supports the hypothesis that the planet’s early environment included large, standing bodies of water—potentially lakes or even ancient oceans.
Ancient Corals: Signatures Beyond Mineral Formation
Scientists have long debated whether certain mineral formations on Mars are purely geological or could be remnants of biological activity. The coral-shaped structures are notable because their morphology diverges from typical mineral deposits, showing layered textures and complex shapes indicative of biological processes. This raises the exciting possibility that these are the fossils or fossil-like remnants of life forms that once thrived in a watery environment billions of years ago.
Implications of the Discovery: Evidence of Ancient Martian Life?
What Does This Mean for Martian History?
If these coral-like formations are indeed ancient biological structures, it signifies that Mars was not only temporarily habitable but also supported complex life. The age of these formations, estimated to be billions of years old, places them in a period when Earth was also teeming with underwater life, including early coral reefs and other multicellular organisms.
This discovery aligns with the broader narrative that Mars was once a vibrant, water-rich planet. Evidence of water, such as mineral deposits and sedimentary layers, has already suggested a history of liquid water on Mars. The coral-like structures now provide a tangible, morphological link to this watery past, reinforcing the hypothesis that life could have possibly emerged there, just as it did on Earth.
The Role of Remote Sensing and Rover Missions
How Did Scientists Come to This Conclusion?
Advanced imaging techniques, spectrometers, and rover-mounted cameras have played pivotal roles in this discovery. NASA’s Curiosity Rover, which has been exploring Gale Crater since 2012, has equipped scientists with high-resolution images of rocks and sediment layers that indicate the presence of past water activity. Similarly, the ChemCam instrument has provided compositional data revealing mineral signatures compatible with biological activity.
Additional analysis of these formations by the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory’s team identified features consistent with biological structures, further bolstered by previous findings of clay minerals and sulfates—both of which form in watery environments. These details collectively paint a compelling picture of Mars’ ancient environment as a potentially life-supporting habitat.
Additional Evidence Supporting Ancient Marine Ecosystems
- Research on Rock Shapes Similar to Coral: High-resolution images capture rocks that resemble coral colonies, suggesting biological origins.
- Signs of Water-Related Mineral Deposits: Minerals such as clays and sulfates, known to form in aqueous settings, reinforce the idea of a water-rich past.
- Detection of Microstructures Resembling Reefs: Micro- and macrostructures identified within rock layers lend credence to the hypothesis of sedimentary reef-building activity.
What’s Next in the Search for Martian Life?
Future Missions and Investigations
The discovery of coral-like structures on Mars energizes ongoing and future missions, including the Mars Sample Return initiative and the deployment of more advanced rovers. These missions aim to drill deeper into the Martian crust, analyze samples with greater precision, and search for preserved biosignatures.
Scientists are now encouraged to focus on identifying specific organic molecules and microfossils that could definitively demonstrate biological activity. The potential to find preserved ancient life, akin to what is preserved in Earth’s stromatolites or microfossils, is the next frontier.
Broader Significance: Are We Alone?
The implications of discovering ancient coral-like structures are profound. If confirmed, it would imply that Mars was once a cradle for life, increasing the likelihood that life may have existed elsewhere in the universe. This, in turn, fuels the age-old question—**are we alone?** The possibility that life once flourished in Mars’ watery environment propels astrobiology into a new era of exploration and discovery.
Conclusion: A New Chapter in Martian Exploration
The discovery of multi-billion-year-old coral structures on Mars is an extraordinary milestone. It underscores the importance of planetary geology and astrobiology in understanding the universe’s history. While many questions remain—such as whether these structures are indeed biological, or how widespread water was on ancient Mars—the evidence now strongly suggests that the Red Planet possessed the crucial ingredients for life in its distant past.
As future missions seek to uncover more details, the dream of finding extraterrestrial life becomes more tangible than ever. This discovery fuels our curiosity and showcases how far humanity has come in unraveling the mysteries of our neighboring planets. Mars may hold secrets that can redefine our understanding of life’s origins and the universe’s vast potential for harboring life beyond Earth.
Stay Tuned for More Updates
For more updated news please keep visiting Prime News World.