A Stagnant Market in a Time of Growing Challenges
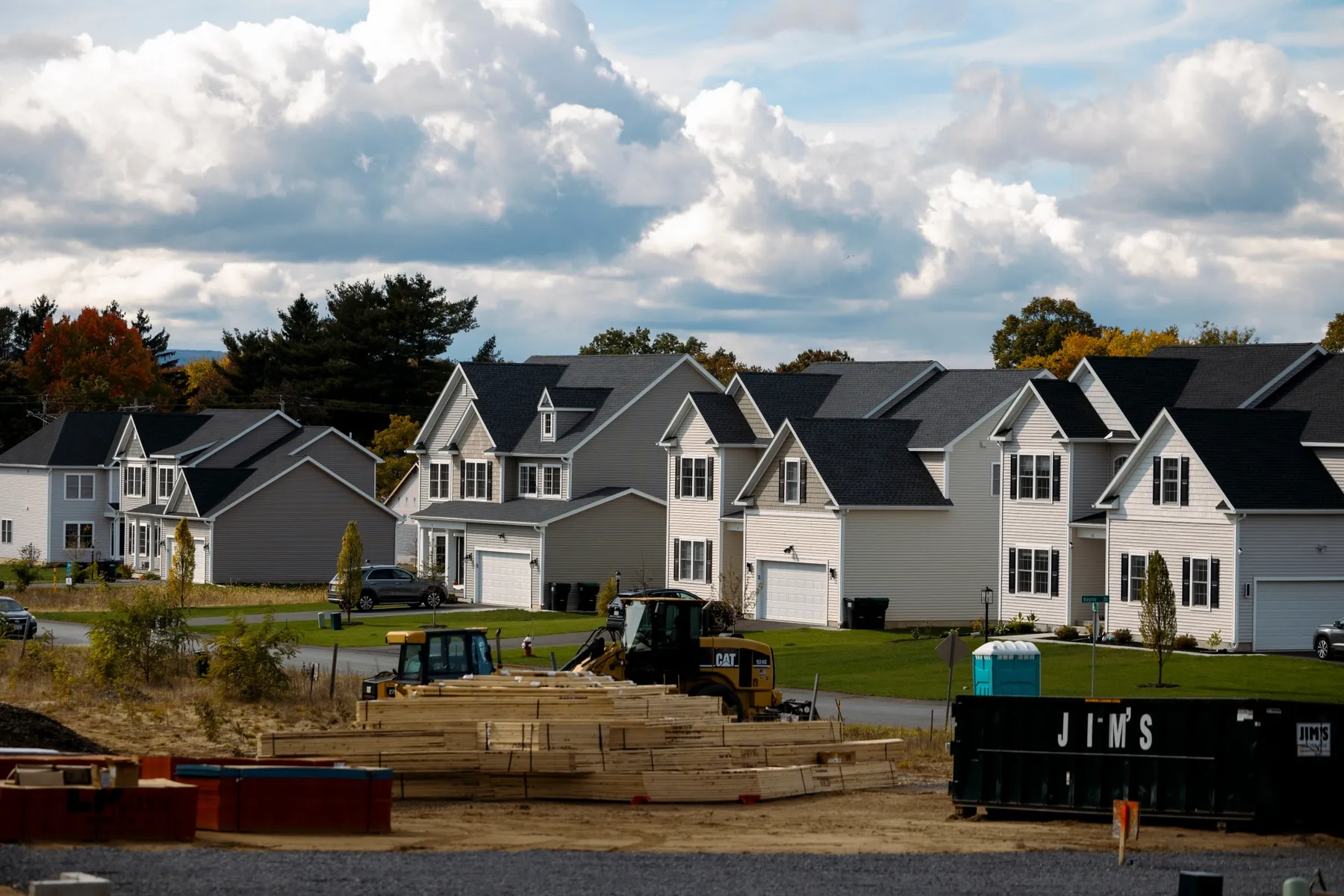
The residential real estate market in the United States is currently experiencing a period of stagnation, particularly in the realm of new home sales. Despite fluctuating economic conditions and ongoing efforts to stimulate growth, the sector remains largely flat, reflecting deeper issues rooted in affordability and accessibility. This plateau signifies more than just a temporary pause; it underscores persistent challenges faced by prospective homebuyers across the nation. As housing costs continue to outpace income growth, many Americans find themselves caught in a cycle of diminishing purchasing power, leading to a slowdown in new home construction and sales activity.
The Current State of New Home Sales in the U.S.
Recent reports from The World Property Journal highlights a clear stagnation in new home sales over recent months. According to reports, the number of newly constructed homes sold has remained steady, signaling a market at a crossroads. While some might interpret this stagnation as a sign of cautious optimism, it is more accurately a reflection of profound affordability issues that continue to plague the housing sector in America.
Factors Contributing to the Market’s Stagnation
Several intertwined factors are responsible for the ongoing plateau in new home sales:
1. Rising Home Prices Outpacing Income Growth
One of the most significant barriers to homeownership is the relentless increase in home prices. According to industry reports, the median price for new homes has escalated significantly over the past few years, often outstripping increases in median household incomes. This disparity creates a challenging environment where many prospective buyers find themselves unable to afford new constructions, despite their interest and willingness to purchase.
2. Mortgage Accessibility and Rising Interest Rates
Interest rates have seen an upward trajectory, adding further strain on potential homebuyers. Higher mortgage rates mean increased monthly payments, which dampen affordability. Coupled with stricter lending standards implemented by financial institutions following economic uncertainties, qualifying for a mortgage has become more arduous for many Americans.
3. Limited Housing Inventory
A shortage of available new homes, particularly in popular markets, has also contributed to the stagnation. Builders are cautious amid rising materials costs and regulatory hurdles, leading to slower development. This tight inventory limits choices for buyers and keeps prices elevated, feeding into the cycle of limited affordability.
The Broader Economic and Social Implications
The stagnation in new home sales is not merely a market statistic; it has tangible implications for the broader economy and societal well-being.
- Economic Growth Concerns: The housing sector is closely linked to overall economic vitality. A slowdown in new home construction can lead to reduced employment, lower demand for related goods and services, and overall sluggish economic growth.
- Generational Challenges: Younger generations, including Millennials and Gen Z, face difficulties entering the housing market. The inability to afford new homes delays wealth accumulation and long-term financial stability, potentially impacting social mobility and economic equity.
- Urban and Community Development: Limited new housing constrains urban expansion and infrastructure development, potentially exacerbating housing shortages, crowding, and rising rental prices in urban centers.
What Does the Future Hold?
While the current landscape suggests ongoing challenges, some analysts believe that market adjustments could occur as builders, policymakers, and financial institutions respond to the affordability crisis. Potential developments include:
– Policy interventions aimed at reducing regulatory barriers and promoting affordable housing projects.
– Innovations in construction technology reducing costs of new homes.
– Programs designed to assist first-time buyers and low-to-moderate-income families.
However, these solutions require concerted efforts and time to materialize. In the short term, the market is expected to remain relatively stagnant, showcasing a landscape where demand is constrained by affordability rather than lack of interest.
Conclusion: Navigating the New Normal
America’s housing market is at a pivotal juncture. The recent plateau in new home sales underscores the deep-rooted challenges of pricing, financing, and inventory that continue to hinder prospective buyers. Addressing these issues necessitates comprehensive strategies involving policymakers, builders, and financial institutions alike. Meanwhile, prospective homebuyers must navigate a complex environment where affordability remains the key obstacle.
As the market adapts to these ongoing challenges, staying informed and proactive is crucial for all stakeholders. The hope is that with strategic interventions, the market can reignite growth and make homeownership more accessible in the years ahead.
For more updated news please keep visiting Prime News World.